Deliver it 14/21 days
MORAVIAN G0-0300 CCD CAMERA WITH SONY ICX424 SENSOR TO CCD MONO
The G0 Moravian cameras with the latest CCD technology are the best price/quality choice for astrophotography of the Solar System and bright deep sky objects; they work in low light conditions with very high sensitivity, very low noise, fast image download, electronic shutter and integrated autoguider port to guide the telescope mount in astrophotography.
| Carrier | Description | Estimated Delivery | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Home delivery - International | Home delivery - International |
Friday, 16 May - Friday, 23 May |
|

Home delivery - International
Home delivery - International
Estimated delivery:
Friday, 16 May - Friday, 23 May
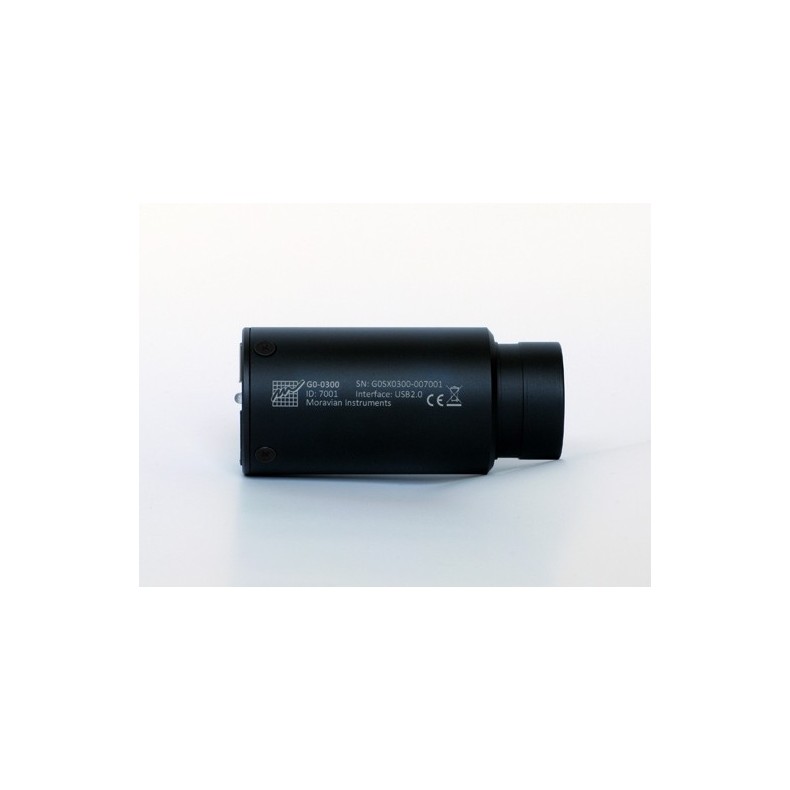
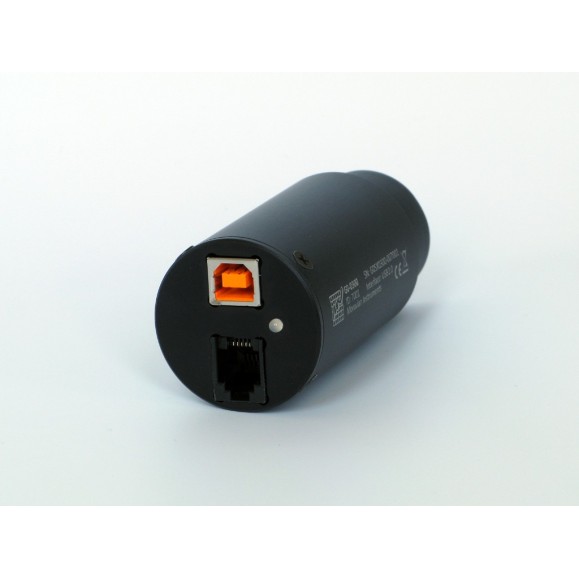
CCD Camera Moravian G0-0300 with Sony ICX424 AL CCD Mono Sensor
The G0 series of CCD cameras is based on Sony ICX CCD detectors. The cameras are powered from USB, so they are connected to the PC with a single cable. The standard "Autoguider" port allows the camera to directly control the movement of the telescope. The G0 cameras have dimensions similar to those of a 1.25" eyepiece.
G0 cameras are very compact, lightweight and easy to operate. The user only needs to insert it into the telescope's eyepiece holder, plug the USB cable into the computer and it works.
Sensitivity is an important feature of any guidance camera. It must provide images of guide star(s) with a sufficient S/R ratio in a fairly short time to ensure perfect guidance. The need to accumulate light for many tens of seconds or even minutes is often unacceptable for high quality guiding. This is why G0 cameras use Sony ICX high sensitivity CCDs.
Sony EXview HAD CCD has a quantum efficiency of over 50% and low readout noise.
G0 cameras support 16-bit digitization, significantly improving dynamic range.
Strong blooming protection keeps even the brightest stars round, with no saturation spicules.
G0 cameras also provide very fast readout: pixel digitization speed reaches 8 MPx/s in fast readout mode.
G0 cameras offer a round body, which is more compact compared to the G1 series, which is important, for example in combination with an off-axis guide.
The G0 cameras do not require any external power supply, they are powered entirely from the computer via the USB cable. Because the power provided by the USB line is quite limited, these cameras do not use a power-hungry Peltier cooler.
G0 cameras are USB-powered devices (only 1 cable is needed to operate).
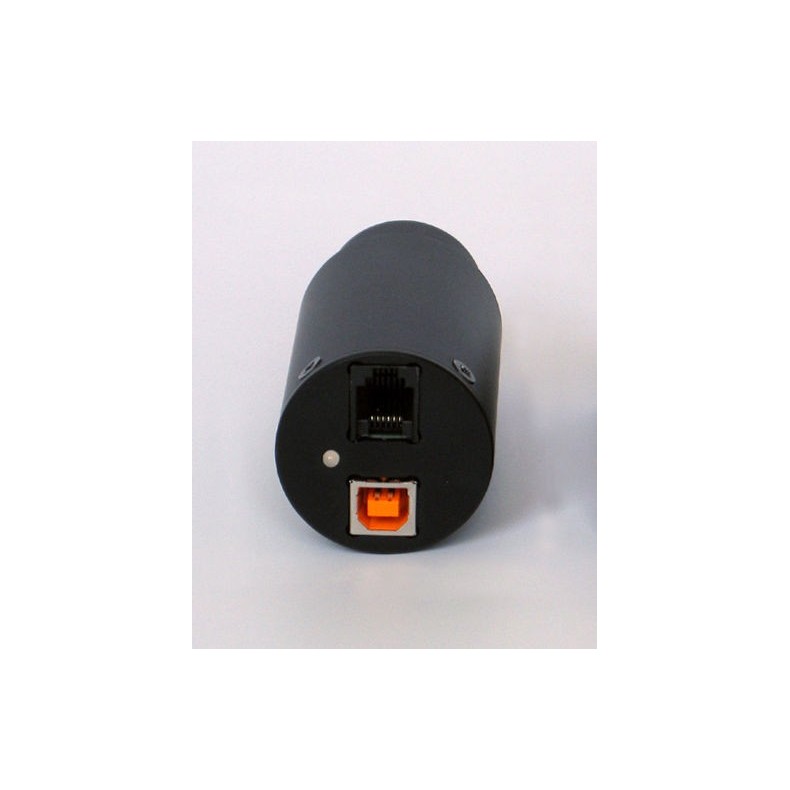
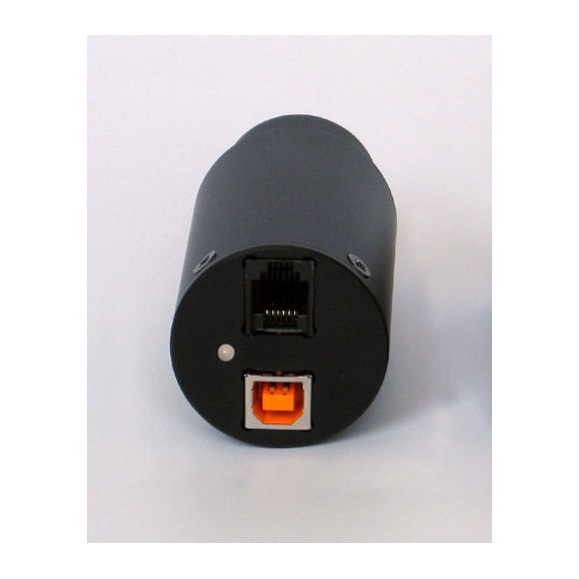
Although modern astronomical telescope mounts support PC connection, G0 cameras incorporate a standard 6-pin connector for autoguider input. Therefore, the computer can guide the mount through the camera, even in the case where there is no link between the telescope mount and the PC. (The G0 camera body is equipped with a standard Autoguider connector)
Note: The current of the autoguider port should not exceed 150 mA. If the mount does not treat the autoguider port as "logic input" only, but switches the guiding motors directly by these signals, a "relay box" must be inserted between the camera and the mount. The relay box ensures the switching of the currents required by the mount.
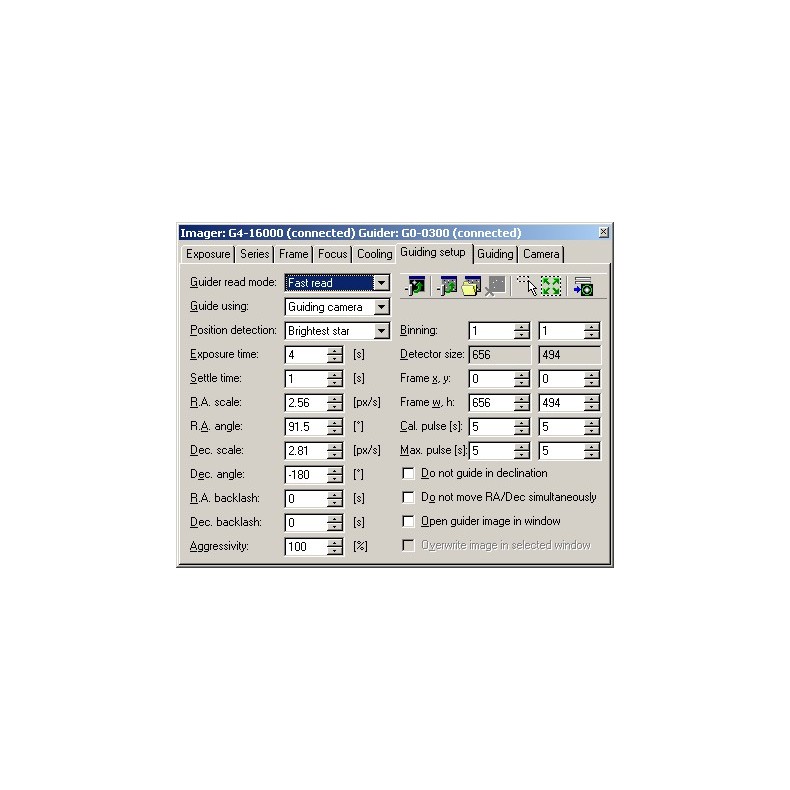
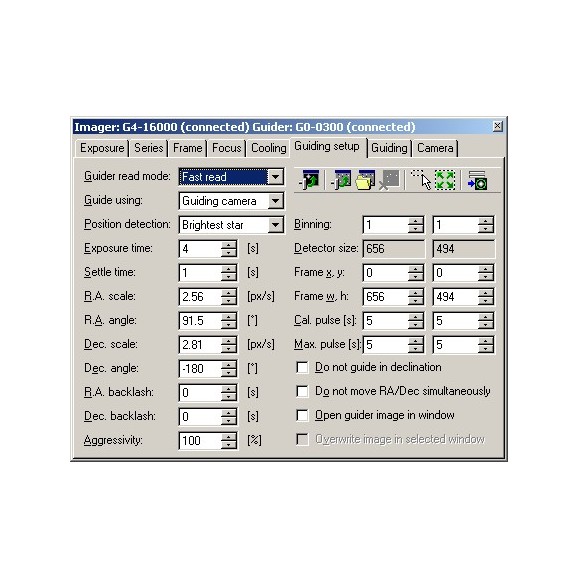
The SIPS (Scientific Image Processing System) control software supports guidance through the camera port as well as through the PC link to the telescope.
Note: The G0 series of CCD cameras requires SIPS v2 or higher version to operate.
The Autoguider port on the G0 camera body follows the standard pinout of the ST-4 guiding cameras, as the G0 series of CCD cameras are designed for guiding as well as CCD imaging, either astronomical or microscopic.
The SIPS control software treats any CCD camera as an imaging or guiding device. The user chooses which camera will be used for imaging and which will be used for guiding.
While the monochrome CCD captures all incoming wavelengths (to which the detector is sensitive), the color CCD detector has red, green and blue filters applied on individual pixels, arranged in a so-called Bayer mask. The monochrome CCD is substantially more sensitive, but multiple exposures through color filters are necessary if color images are to be captured. On the other hand, the color detector limits the incoming light through the color filters, but allows reconstruction of the color image from a single exposure, even if the color resolution is lower than the CCD pixel array.
Although so-called full-frame (FF) CCDs achieve the highest sensitivity, they can only be used in conjunction with a mechanical shutter; in contrast, so-called interlinear transfer (IT) CCDs are equipped with an electronic shutter, which allows very short exposures. This is why G0 cameras use IT detectors. Furthermore, IT sensors differ in terms of image readout: while progressive readout chips can read all pixels of the image at once, interleaved readout CCDs divide the frame into two half-frames containing only odd or even rows and read the text independently.
G0 guidance cameras are designed to work in cooperation with a computer (PC). The guiding algorithms are performed by the PC, not by the camera itself. To operate the camera, a PC with a 32-bit or 64-bit Windows operating system with at least one free USB port is required.
Note: Linux drivers are also available. Please contact us if you are interested in Linux drivers.
Technical Specifications
CCD chip
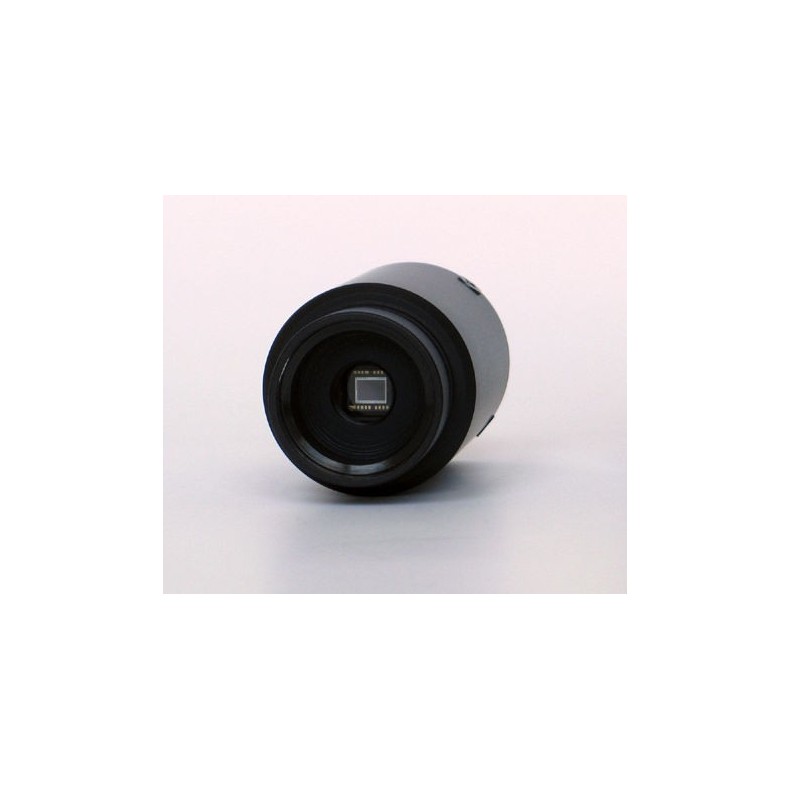
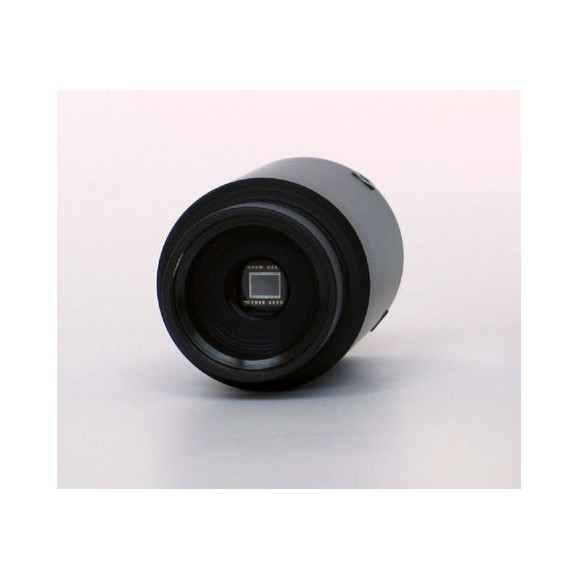
G0 cameras use sensitive, low-noise Sony ICX CCD detectors with estimated quantum efficiency (QE) exceeding 50%. The dark current and read noise of these CCDs are very low. Model G0-0300 uses Sony's ICX424AL VGA (640 × 480 pixels) VCD chip with progressive readout.
- Resolution: 656 (H) × 494 (V) pixels
- Pixel size: 7.4 μm (H) × 7.4 μm (V)
- Image area: 4.9 mm (H) × 3.7 mm (V)
- Discharge time: ~ 0.05 s
Camera electronics
The 16-bit A/D converter with correlated double sampling guarantees a high dynamic range, which in fact exceeds the electron well capacity of each CCD pixel. The fast USB interface guarantees image download time in fractions of a second.
The maximum length of the USB cable is 5m. This length can be extended, for example, to 10 m using a USB hub or USB extender cable. An extension of up to 100 m can be achieved with extenders.
- Resolution: ADC 16 bit
- Sampling method: Double correlated sampling.
- Readout modes: fast (8 Mpx / s) // slow, with very low electronic noise (2.5 Mpx / s)
- Sub-frame readout: Yes
- Computer interface: Hi-Speed USB 2.0, compatible with USB 1.1 Full Speed
Note: SIPS control software allows resizing by changing the binning via software if lower resolution images are desired.
Chip cooling
The G0 series CCD cameras do not use active cooling with Peltier TEC modules, so the CCD cannot be cooled below ambient temperature, but they do include the integrated temperature sensor, which measures the current temperature of the CCD. This feature allows to control the temperature of the CCD and to ensure that the dark frame used was taken at the same or similar temperature to scientific shots that have had light exposure.
Power supply
G0 cameras are powered from the USB cable. No external power supply is required.
The current limit for a single USB device is 500 mA at 5 V power supply. The current required by the G0 cameras does not, in any case, reach the 500 mA limit, defined in the USB specification.
Note: Some USB cables incorporate very fine electrical lines with relatively high resistance. If the USB device consumes several hundred milliamps, the voltage drop across the USB cable may be around one volt. Although the G0 camera should work, some features may be adversely affected. Always make sure that the USB cable used is as short as possible and with low resistance electrical lines.
Mechanical specifications
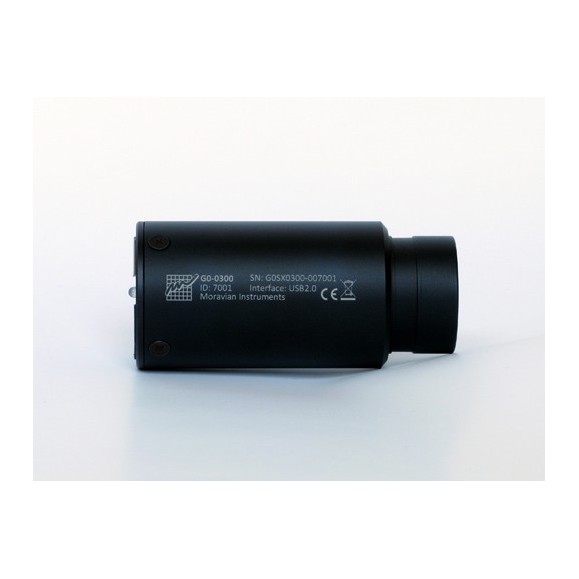
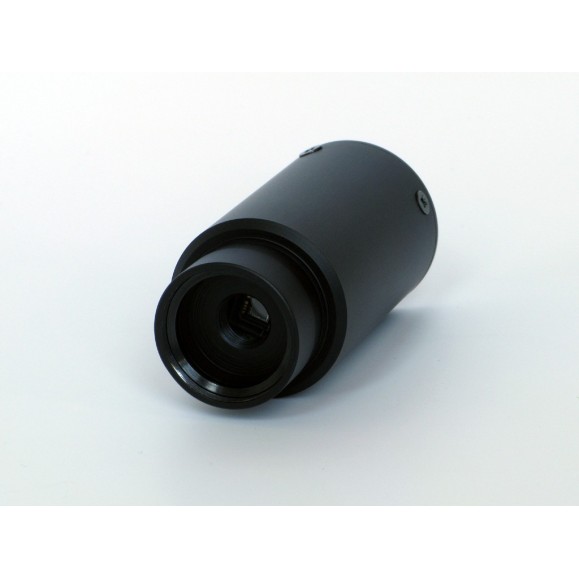
The cylindrical camera body is 40 mm in diameter and 85 mm long, of which 18 mm is a 1.25 "(31.7 mm) adapter and 67 mm is the camera body. The body is CNC machined from high quality aluminum and anodized black.
G0 cameras use interline transfer CCD and do not contain a mechanical shutter. It is necessary to manually cover the telescope to take a dark or bias (offset) frame.
- Internal mechanical shutter: No
- Shortest exposure time: 0,125 s
- Longest exposure time: limited only by chip saturation
- Camera Length: 85 mm (of which 18 mm is 1.25" adapter)
- Camera diameter: 40 mm
- Camera weight: 0.1 kg
Note: The 1.25" adapter is an integral part of the G0 camera body and cannot be removed and replaced with another adapter.
Guidance
Although the G0 series CCD cameras are capable of capturing images of various objects in astronomy, microscopy or other low light imaging applications, they are primarily intended for guiding telescope mounts using G2, G3 or G4 cameras as the main camera for scientific purposes.
The G0 camera can function as a "remote guiding body" for any CCD camera, including the Gx series. The fact that it is not connected to the Gx camera body by any proprietary cable, but directly to the USB port of the PC, brings numerous advantages:
- The guiding camera can guide any astronomical camera or digital SLR camera, not just the main camera type for which it is designed.
- There are no proprietary connectors / cables to connect the main camera to the remote body. Instead, a standard USB cable is used.
- There is virtually no limit to the distance between the guiding camera and the scientific imaging camera, so the guiding camera can be placed on any guiding telescope or off-axis guide.
- Even if the guiding camera shares the same telescope with the main camera - using an off-axis guide - the light feeding the guiding camera is deflected before it passes through the filters, so there is enough light to guide even when the main imaging camera takes the exposure through some very "dark" filters, such as UV, Blue or Hα.
- Moreover, the USB hub is able to create an integrated solution for two Gx and G0 cameras that previously operated separately.
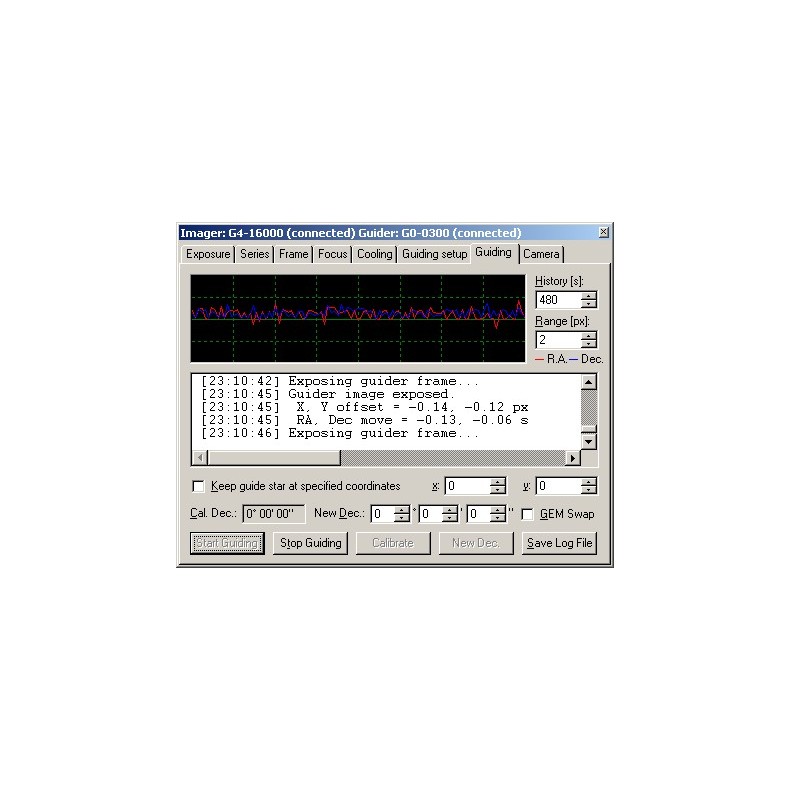
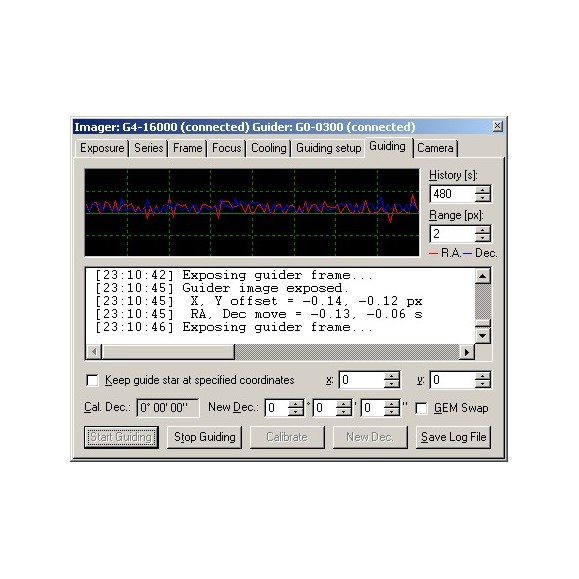
SIPS guidance software:
The G0 guiding camera connects directly to the USB port of the PC or USB hub, without requiring a "CPU box" or similar device. The guidance algorithms are performed on the PC itself, and since the CPU used by a PC is several orders of magnitude more powerful than any embedded CPU that can be used in any CCD camera, the guidance algorithms can be much more sophisticated. Such algorithms are implemented in the SIPS camera control software.
There are two algorithms used in SIPS for guiding:
- Single-star guiding. The PC calculates the centroid of the brightest star in the image acquired by the guiding camera. The centroid position is computed with an accuracy of fractions of a pixel, so guiding can be very accurate even when the guide is attached to a short focal length telescope.
- Astrometric reduction guidance. The PC performs basically the same operation as in the case of multiple-exposure sub-pixel matching or astrometric reduction. The number of triangles are created from the brightest stars and matched with triangles in the reference frame. Triangle matching requires at least three stars in the guiding image and is therefore suitable for either short focal telescope-guiding or rich star fields; the image offset is calculated from multiple star positions and is less sensitive to random errors arising from poor seeing, blooming spicules, etc.
The SIPS guiding support allows the incorporation of the Autoguider port of the G0 camera which is de facto standard and compatible with various telescope mounts. SIPS can also guide through the telescope link itself (e.g., through the Meade LX-200 or Celestron Nexstar protocol), so an autoguider cable may not be necessary, but a specialized guiding device such as the G0 camera guide can generally control the mount with much better accuracy compared to the relatively limited time resolution of an application running on the PC.
CCD camera Moravian G0-0300 with Sony ICX424 AL CCD Mono sensor